Functional sRNAs Unleashed:
Isolate What Matters with TraPR Small RNA Isolation Kit
TraPR Small RNA Isolation Kit
TraPR (Trans-kingdom, rapid, affordable Purification of RISCs) presents a gel- and bias-free, column-based method for isolating functional small RNAs from RNA-induced silencing complexes (RISCs) of all organisms. Within 15 minutes, TraPR enables purification of RISC fractions even from challenging or inconsistent samples, cell types, tissues, and biofluids. The TraPR Small RNA Isolation Kit generates high-quality sRNA suitable for Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) applications and thus provides a highly reproducible, time-saving method that outperforms all current gold-standard procedures for sRNA profiling.
TraPR Small RNA Isolation Kit seamlessly integrates with Lexogen’s miRVEL sRNA Library Preparation Kits, ensuring a streamlined and user-friendly workflow for small RNA-Seq analysis from start to finish.
Performance
TraPR Eliminates the Need for Gel Extraction of sRNAs
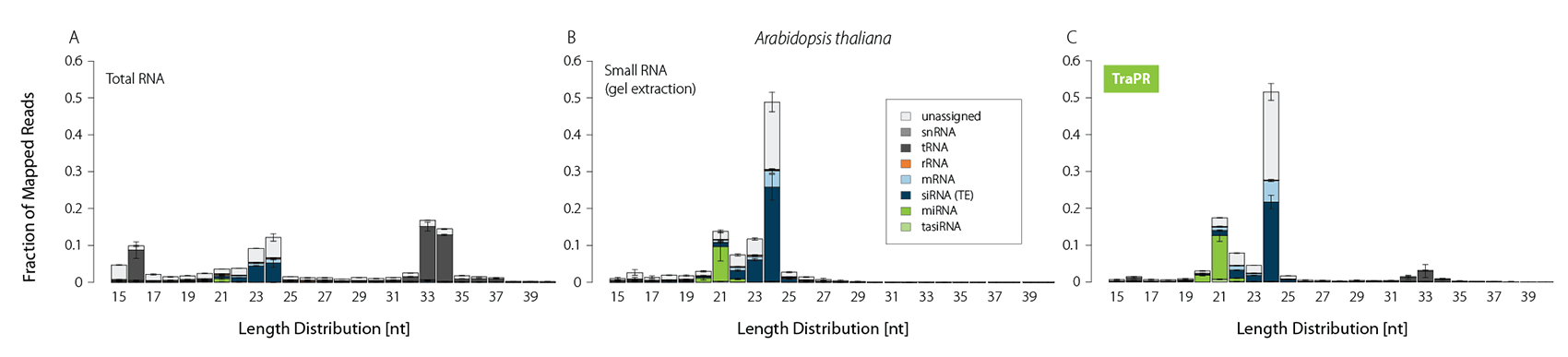
Typically, sRNA-Seq libraries from total RNA contain only a minor fraction of reads corresponding to functional sRNAs (Fig. 1A). Thus, size selection methods such as gel extraction are commonly applied to increase the share of sRNA-mapping reads (Fig. 1B). TraPR replaces these lengthy and error-prone gel extractions with quick and easy column purifications (Fig. 1C).
Figure 1 | TraPR enriches functional sRNA without the need for gel extraction. Size distribution and biotypes of mapped reads from NGS libraries prepared from A) total RNA (TRIzol extraction), B) gel-purified, or C) TraPR-isolated sRNA from Arabidopsis thaliana. Adapted from Grentzinger et al., 2020.
Universal and Species-Independent sRNA Isolation
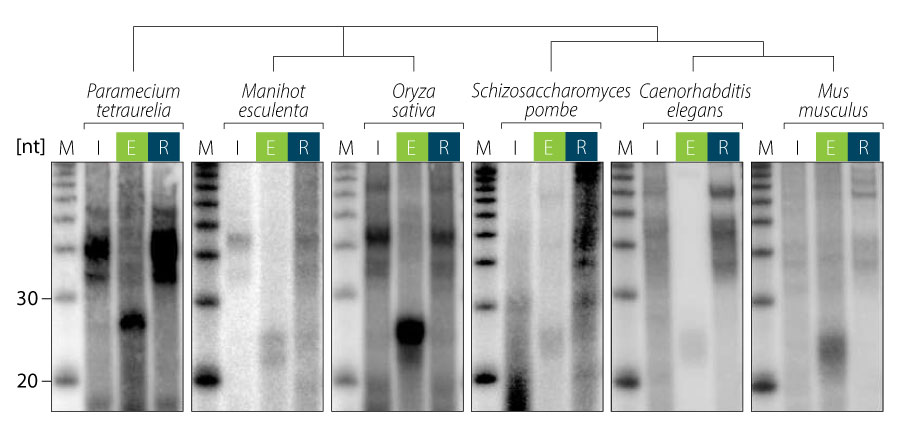
The TraPR Small RNA Isolation Kit easily isolates all RISC-associated sRNAs found in any organism, tissue, cell type, or biofluid. No previous characterization or knowledge of the organism of interest is required (Fig. 2).
Figure 2 | TraPR isolation of RISC-associated sRNAs exemplified for ciliate, plant, yeast, nematodes, and mammalian samples. RNA was extracted from input (I), TraPR eluate (E), and column-retained (R) fractions, radiolabeled and analyzed by gel electrophoresis and autoradiography. Adapted from Grentzinger et al., 2020.
High-Quality sRNA Isolation from Challenging and Degraded Samples
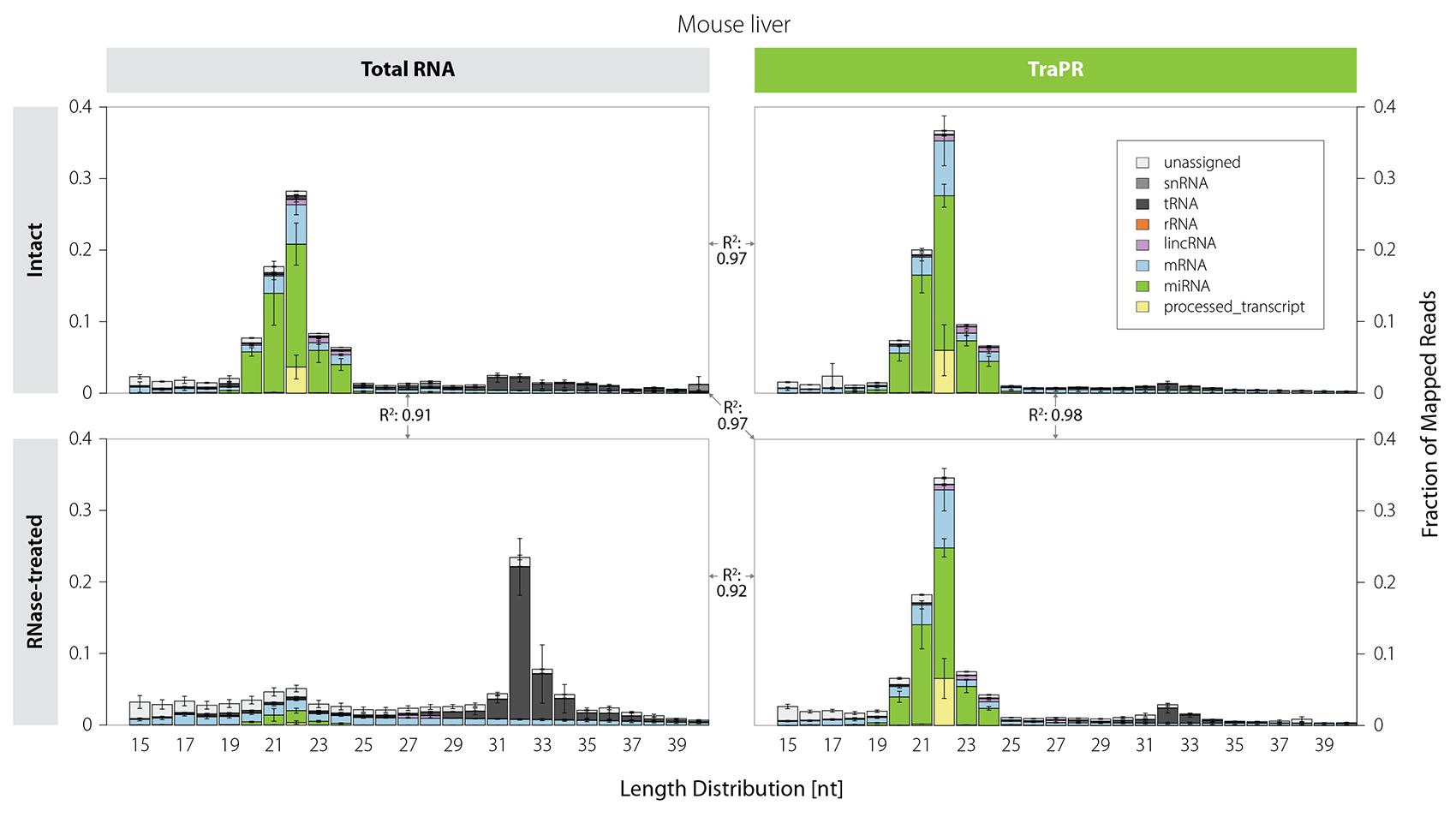
Size-based selection does not distinguish between functional sRNAs and short RNA fragments originating from degradation. Thus, sRNA library preps from samples that are prone to RNA degradation are often heavily contaminated with tRNA-, mRNA-, and rRNA-derived fragments (Fig. 3, left). In contrast, TraPR isolation preserves the sRNA size distribution even for RNA-degraded samples (Fig. 3, right).
Figure 3 | TraPR enables clean isolation of high-quality sRNA from RNA-degraded samples. Mus musculus liver lysates were treated for 30 minutes with RNase T1 to simulate RNA degradation. Size distribution and biotypes of mapped reads from NGS libraries prepared from Total RNA (TRIzol extraction) or TraPR-isolated sRNA from intact or RNase-treated samples. The R² values between the panels refer to the respective miRNA read count correlations. Adapted from Grentzinger et al., 2020.
Efficient Enrichment of Low-Abundant miRNAs e.g. from Plasma
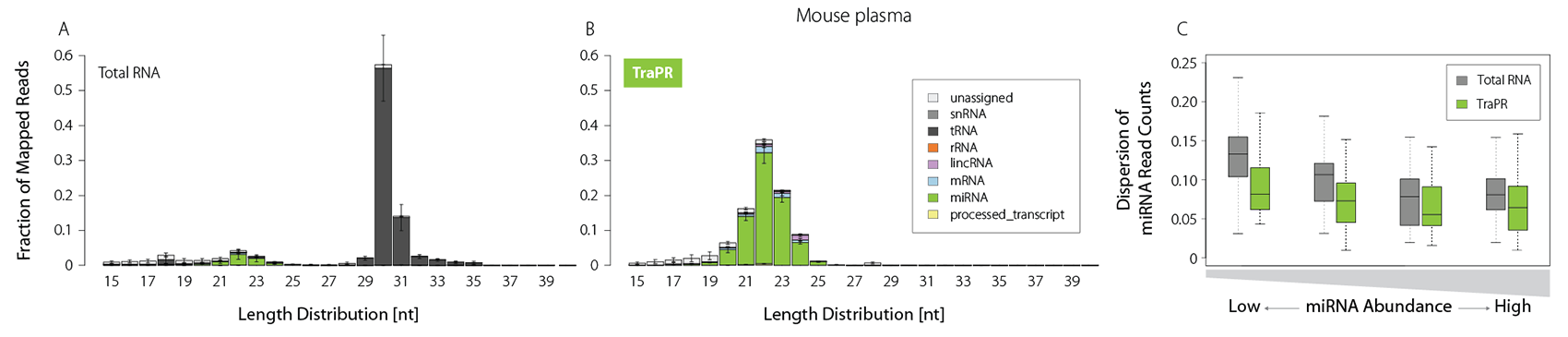
Plasma is of growing interest for biomarker discovery, but it is often prone to RNA degradation and/or contains only minute amounts of sRNAs. TraPR enriches sRNAs even from such challenging samples by one order of magnitude (Fig. 4A and B).
It further reduces the read count dispersion particularly for low-abundant miRNAs, enabling precise quantification (Fig. 4C). Small RNA isolation from liquid samples thereby becomes easily accessible, and TraPR is perfectly suited for biomarker discovery applications.
Figure 4 | TraPR robustly detects low-abundant sRNA from plasma samples. Total RNA (TRIzol) or TraPR-isolated RNA from 150 µl Mus musculus plasma were converted to NGS libraries and sequenced. A) and B) Size distribution and biotypes of mapped reads. C) Box plot representation of miRNA NGS read count dispersion, grouped by miRNA abundance. Adapted from Grentzinger et al., 2020.
Consistent Performance Over a Wide Input Range without the Need for rRNA Depletion
Small RNA profiling of certain tissue types requires extensive and laborious sample preparation. In Drosophila ovaries, for instance, the 30 nt long 2S rRNA is highly abundant. Therefore, a typical piRNA library generation from fly gonads is a two- to three-day process of gel-based size selection, customized depletion, and oxidation of 2S rRNA and other abundant RNA fragments. While oxidation effectively removes contaminants, it also eliminates the majority of miRNAs. In contrast, sRNA isolation using TraPR fully preserves miRNAs, siRNAs, and piRNAs without requiring depletion of contaminating non-regulatory RNAs (Fig. 5). Furthermore, TraPR can be used over a broad input range starting from as little as two ovary pairs.
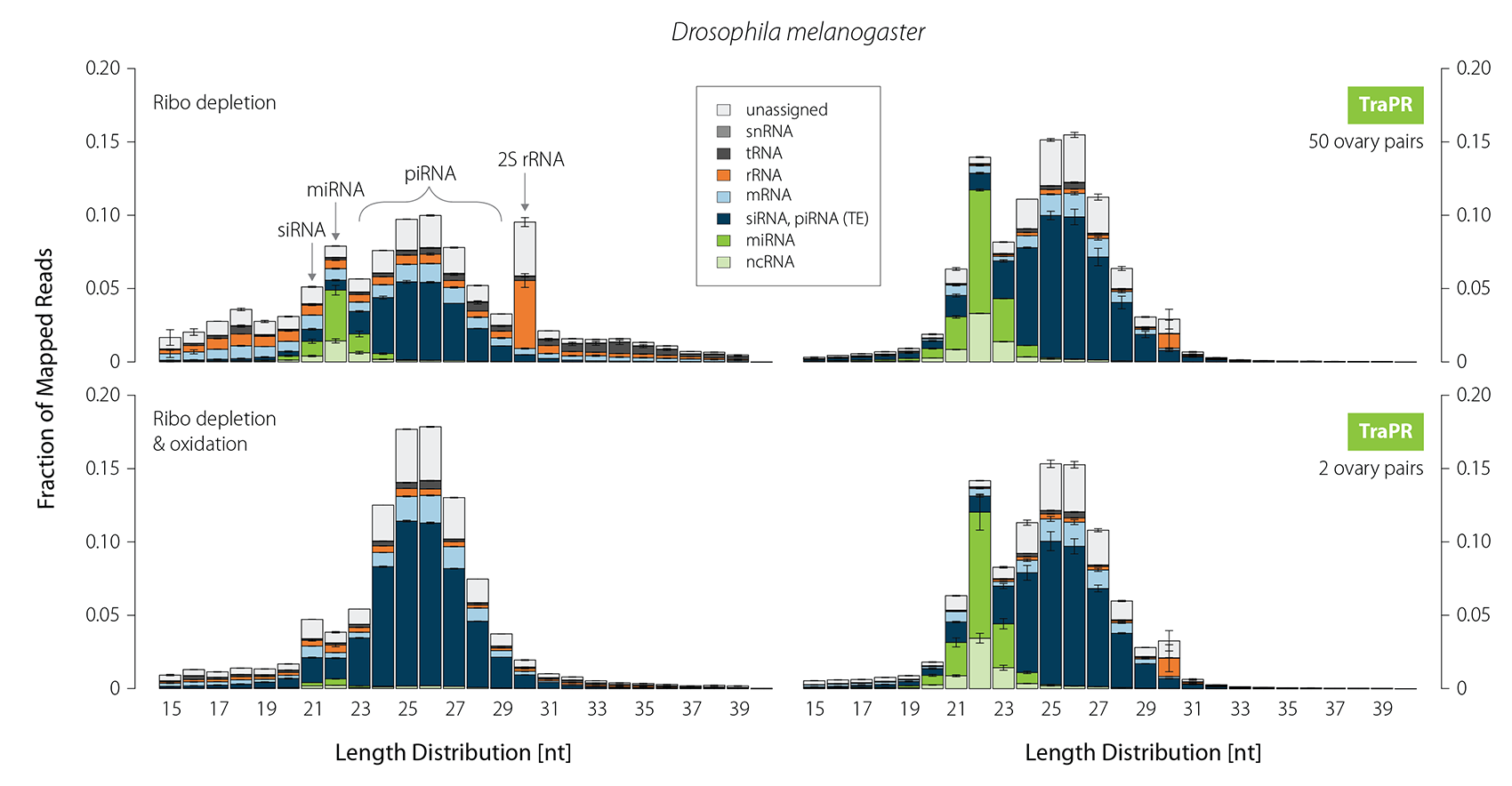
Figure 5 | TraPR robustly enriches all classes of sRNAs while eliminating 2S rRNA from Drosophila ovaries. Size distribution and biotypes of mapped reads from NGS libraries. 10 µg of total RNA were used for gel selection followed by ribo-depletion (+/- oxidation). For TraPR-based isolation only two or 50 ovary pairs were used as input. Adapted from Grentzinger et al., 2020.
Reference
Grentzinger T., Oberlin, S., Schott, G., et. al. (2020) A universal method for the rapid isolation of all known classes of functional small RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res, DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaa472.
Testimonials
Workflow
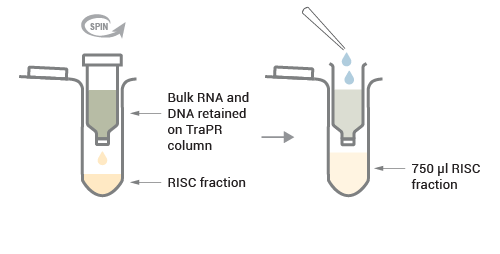
The TraPR input fraction (clarified lysate) is loaded onto the prepared TraPR column and mixed vigorously.
Pure RISCs loaded with their cognate sRNA are eluted from the column with TraPR Elution Buffer (TEB) while bulk RNA and DNA are retained on the TraPR column.
Small RNA is isolated from RISCs using acidic phenol / chloroform. Subsequently, sRNA is precipitated with isopropanol, washed, and solubilized in RNA Elution Buffer (REB).
Featured Publications
FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions
Access our frequently asked question (FAQ) resources via the buttons below.
Please also check our General Guidelines and FAQ resources!
How do you like the new online FAQ resource? Please share your feedback with us!
Downloads
Safety Data Sheet
If you need more information about our products, please contact us through support@lexogen.com or directly under +43 1 345 1212-41.
Ordering Information
| Cat. No. | Product Name |
| 128.08 | TraPR Small RNA Isolation Kit, 8 preps |
| 128.24 | TraPR Small RNA Isolation Kit, 24 preps |
First time user of TraPR
First Time User? We’re excited to offer you an exclusive introductory offer.
Buy from our Webstore
Need a web quote?
You can generate a web quote by Register or Login to your account. In the account settings please fill in your billing and shipping address. Add products to your cart, view cart and click the “Generate Quote” button. A quote in PDF format will be generated and ready to download. You can use this PDF document to place an order by sending it directly to sales@lexogen.com.
Web quoting is not available for countries served by our distributors. Please contact your local distributor for a quote.